Nationalpark Hunsrueck Hochwald/en: Unterschied zwischen den Versionen
Tschug (Diskussion | Beiträge) |
Tschug (Diskussion | Beiträge) |
||
| Zeile 69: | Zeile 69: | ||
</ul> |
</ul> |
||
| − | == |
+ | == Contacts == |
| − | ''' |
+ | '''Ministry for the Environment and Consumer Protection'''<br /> |
| − | + | Dept. D/3 Agriculture, Fishing and Environmental Education<br /> |
|
Dr. Volker Wild<br /> |
Dr. Volker Wild<br /> |
||
| − | [mailto:v.wildk@umwelt.saarland.de |
+ | [mailto:v.wildk@umwelt.saarland.de Email]<br /> |
| − | + | Phone: +49 681 501-4747<br /> |
|
Version vom 24. März 2022, 07:47 Uhr
Hunsrück–Hochwald National Park in Rhineland-Palatinate and Saarland (February 2015)
Photo: K. Funk
Viewer
Go to map service ‘ Hunsrück-Hochwald National Park (Saarland section)’
Go to map service ‘Hunsrück-Hochwald National Park (total area)’
Description
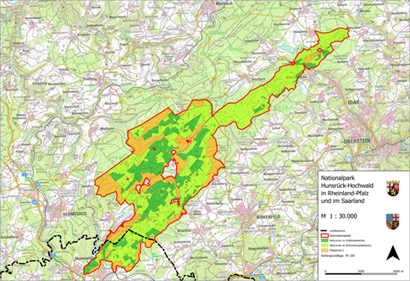
Rhineland-Palatinate and Saarland have signed a state charter to create a transboundary national park covering a total area of roughly 10,000 ha within the two states. The corresponding legislation was passed by the state parliaments of Saarland and Rhineland-Palatinate in late 2014/early 2015. Around 985 ha of the national park lies within the boundaries of the local government areas of Nohfelden and Nonnweiler. This region, which is located in Saarland, is shown on a topographic 1:10,000 scale map and a boundary 1:2,000 scale map (split over 8 sheets).
The thematic map shows the area that is valid for subsidiary protection as a national park in Saarland pursuant to section 24 of the Federal Conservation Act. This area is subdivided into the nature zone, consisting of nature zone 1a (untouched areas, dark green) and nature zone 1b (development areas, light green). This colour coding is intended to represent the varying level of man-made intervention in these two areas. In nature zone 1a (untouched areas), all forest management work has been discontinued and the forest has been left to its own devices. In nature zone 1b (development areas), the aim is to remove non-native species (and especially conifers) and thereby reconfigure the forest so that nature can take over and develop communities of forest species that are typical for the region. Overall, a maximum time frame of 30 years is allowed for nature zone 1b to develop into nature zone 1a.
Ultimately, nature zone 1a will then cover 75 percent of the park’s total area, so as to meet the IUCN’s international criteria for national parks. Nature will then be left to itself in this area.
The remaining area, making up 25 percent of the park, is assigned to buffer zone 2. This zone is intended to protect the nature zone against negative impacts from neighbouring territories. In this zone, upkeep and development measures can be carried out, which can also include supplying local populations with firewood, for example. Since the boundary map and the corresponding map service allow the identification of individual cadastral parcels, landowners can determine the exact extent – if any – to which they are affected by this project.
The boundary map and thematic map are fundamental to the creation of the Hunsrück-Hochwald National Park (Saarland section).
Relevant legislation for the Hunsrück-Hochwald National Park includes the following:
- the Act of Ratification for the State Charter between the States of Rhineland-Palatinate and Saarland Concerning the Creation and Maintenance of Hunsrück-Hochwald National Park
- the State Charter between the States of Rhineland-Palatinate and Saarland Concerning the Creation and Maintenance of Hunsrück-Hochwald National Park
- the topographic map and
- the boundary map for the Hunsrück-Hochwald National Park
Saarland’s Act of Ratification for the State Charter between the States of Rhineland-Palatinate and Saarland Concerning the Creation and Maintenance of Hunsrück-Hochwald National Park can be viewed here ( State Charter).
Hunsrück-Hochwald National Park
The transboundary Hunsrück-Hochwald National Park offers a unique natural environment, characterised by ancient beech woods, secluded moorlands, vibrant forest floors, stony outcrops and resplendent fields of arnica. ‘Letting nature be itself’ is the Park’s motto. What is meant by this are the natural processes that we humans consciously do not change or interrupt. The wide spaces of a national park are perfect for this kind of development.
While the Saarland section makes up only a tenth of the total area, it is certainly not without its charms. The monumental ring wall is a striking relic of our ancient Celtic ancestors and is particularly popular with Park visitors. The Eisener Forest is an area of outstanding natural beauty and, as a Special Area of Conservation and bird sanctuary, forms part of the European Natura 2000 system of protected sites.
Anyone visiting the national park cannot fail to notice three literal ‘highlights’:
- The Erbeskopf, the highest point of elevation in Rhineland-Palatinate, with the Hunsrückhaus Visitor Centre.
- The Wildenburg, with its fairy-tale crags and forests plus a local game preserve.
- The ‘Ring of the Huns’ and Celtic village in Otzenhausen (Saarland) at the foot of the Dollberg bring the Celts and their history to life.
A reception and information area for visitors is provided at three National Park Gatehouses (in Saarland: Otzenhausen Celtic Park).
Downloads
Topographic map
This is a 1: 10,000 scale map that provides an initial overview of the external border and internal structure of Hunsrück-Hochwald National Park.
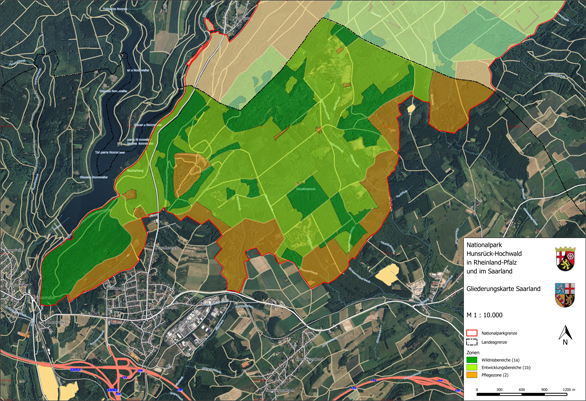
The 1: 2,000 boundary map and the corresponding map service can be used to clearly locate and identify the respective cadastral parcels in terms of their location within the National Park. The division of this map into separate sheets is intended to help with orientation and help with map searches.
Map sheet overview
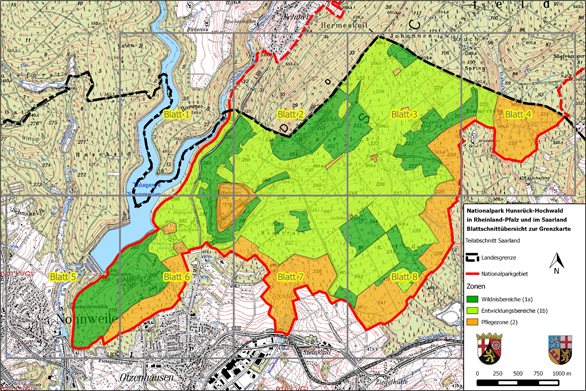
- Download ‘Map sheet overview’
- Download sheet 1
- Download sheet 2
- Download sheet 3
- Download sheet 4
- Download sheet 5
- Download sheet 6
- Download sheet 7
- Download sheet 8
Contacts
Ministry for the Environment and Consumer Protection
Dept. D/3 Agriculture, Fishing and Environmental Education
Dr. Volker Wild
Email
Phone: +49 681 501-4747